2.5. VLF & LF Antenna¶
VLF (Very Low Frequency) Band take place from 3kHz to 30 kHz in the frequency spectrum [18].
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| EM waves penetrate more than higher frequencies such as in the sea water | High background noise levels |
| Low atmospheric attenuation | Communication needs large amount of power at the output of the transmitter |
| Appropriate for long range communication | |
| Diffract around objects that would block higher frequencies | |
| Less prone to multipath |
VLF antennas operate on VLF band. They are electrically small and this simplifies analysis. They are physically large structures. In other words, they generally have a number of towers that 200-300 m high and cover areas of up to a square kilometer or more. The VLF antennas support worldwide communication [18].
The VLF antennas have some problems that listed below [18]:
- Bandwidth is less than 200 Hz.
- Small radiation resistance.
- They are expensive structures.
- Antenna system covers a large area.
- Designing an efficient transmitting antenna is difficult.
- High power levels are needed for transmission.
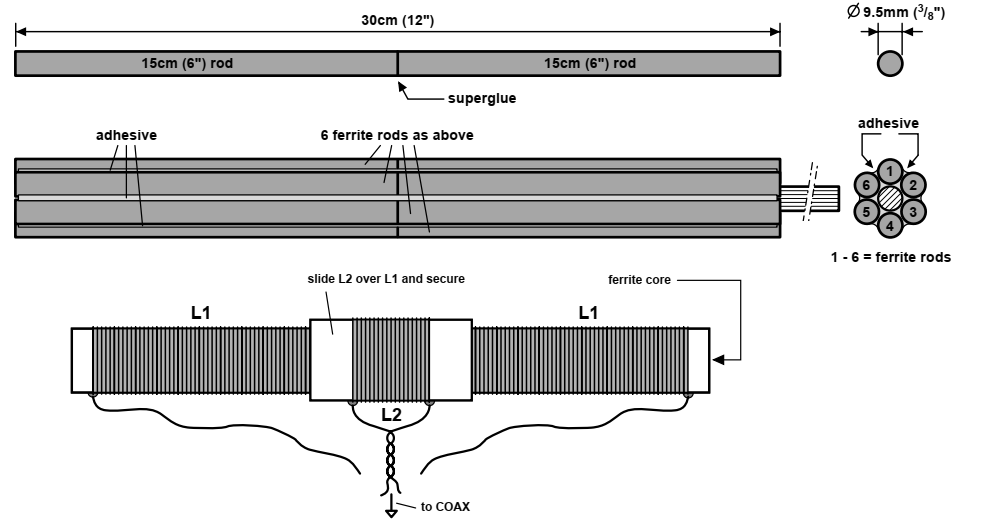
Marris produced a ferrite core loopstick antenna for receiving application as shown in Fig. 2.4. He said VLF antenna but operating frequency band is 50 kHz to 195 kHz, so it was a LF antenna. MMG F14 grade nickel-zinc material was used. The antenna compared with a traditional 20 x 1.25 cm diameter loopstick and he noted that increased signal strength and reduced noise [39].
| 1939 | The Screened Loop Aerial |